Endomorph Body Type Explained

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated

Beginner’s Guide to Healthy Keto & Intermittent Fasting
Receive a step-by-step guide to starting Healthy Keto® and intermittent fasting
Learn about foundational principles and best practices for beginners
Get detailed visual guidance on portion sizes and meal composition
Discover how to set achievable goals and monitor your progress
Find practical tips for overcoming common challenges and staying motivated
Do you have a large, round body frame with wide hips and find it hard to lose weight? You may have an endomorph body type.
Metabolic body types are shaped by the interplay between your metabolism and your nervous system. Understanding your metabolic body type helps to achieve your weight goals and supports health.
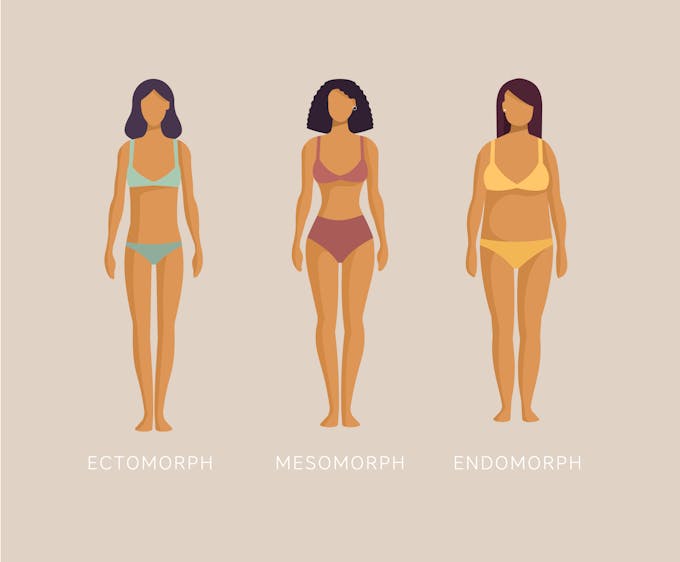
What are the three metabolic body types?
There are the three main metabolic body types:
Ectomorph
Mesomorph
Endomorph
Take a look at the common characteristics of each body type.
Ectomorph
The ectomorph body type typically has a slender body shape, narrow shoulders, and longer limbs than the other body types. Ectomorphs have low muscle mass and tend to have a fast metabolism. They require plenty of energy, explaining why this body type can find it hard to gain weight.
Mesomorph
The mesomorph body type is characterized by a medium-sized frame with broad shoulders and a rectangular skeletal frame. They often have a naturally athletic appearance with moderate body fat and gain muscle mass easily. Mesomorphs have an effective metabolism that helps this body type lose weight quickly.
Endomorph
Endomorph body types generally have a round, larger body frame and are prone to excess weight. This body type has weaker upper body muscles and a tendency for slow metabolism. Endomorphs gain weight easier and find it more challenging to build lean muscle than other body types.

What determines metabolic body types?
Your metabolic body type is determined by your metabolism's effectiveness and overall energy needs.
Genetics is the primary factor determining your basal metabolic rate regulating how quickly and efficiently your body converts fuel to energy. However, lifestyle factors including exercise habits, sleep quality, and diet, can all influence how slow or fast your metabolism works.
Your overall caloric requirements largely depend on your dominant nervous system trait. Your autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functioning, including breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
A balanced nervous system requires both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Your sympathetic nervous system is activated in response to stress. It requires more calories, resulting in a higher need for energy and an increased fat-burning rate.
The calming and muscle-relaxing parasympathetic nervous system counteracts the sympathetic nervous system. It requires fewer calories and preserves your body's energy stores.
Both nervous systems traits regulate body functions. However, most people tend to have one more dominant nervous system trait, which determines your body's overall energy requirements.
The combination of your metabolism and your dominant nervous system influences body fat and body shape which determines your metabolic body type.
Understanding how your metabolic body type influences your body composition can help you reach your health and fitness goals easier.

Endomorph body type explained
Endomorphic bodies typically have a larger skeletal frame and are rounder than other metabolic body types. The endomorph body type indicates a slower metabolism, often resulting in increased fat storage and excessive body weight.
Endomorphs don't tend to develop muscle mass quickly, gain weight easily, and find losing weight challenging.
Endomorph body type characteristics:
Round body frame
Medium to large joints
Weaker upper body muscles
Thick arms
Slow metabolism
Prone to excess body fat around the lower abdomen
Gain weight easily
What diet and exercise benefit endomorphs?
Most endomorphic bodies don’t tolerate carbohydrate-dense foods well and are prone to develop metabolic imbalances, like insulin resistance.
A low-carb diet like Healthy Keto® is an excellent choice for an endomorph diet plan. Research suggests that the ketogenic diet helps weight loss, prevents weight gain, and counteracts a slow metabolism.
The ideal endomorph diet avoids excess calories, carbohydrates, starchy vegetables, sugars, and whole grains. A diet rich in healthy oils, fatty fish, and complex carbs in the form of vegetables supports nutrition and reduces hunger and cravings.
Intermittent fasting (IF) can significantly benefit the endomorphic body type. IF helps to boost metabolism, stimulates your body to burn calories, and supports balanced insulin levels.
Endomorphs can find it hard to lose body fat and increase muscle mass. A fitness program combining high-intensity interval training, weight training, resistance training, and light cardio workouts is ideal for muscle gain and weight loss.
Steady state training (SST) sessions are heart-rate based exercise routines, including walking, hiking, and biking. These types of physical activity are particularly suitable for endomorphic body types, stimulating weight loss and supporting heart health.

Metabolic vs. hormonal body types
Your metabolic body type indicates your basal metabolic rate, how well your body converts food to energy, and your dominant nervous system trait.
In contrast, hormonal body types develop as a result of underlying hormonal imbalances that influence body composition. Hormones profoundly impact your health and affect how your body metabolizes energy and stores fat.
Persistent weight and difficulty to gain muscle mass can be caused by imbalanced hormone levels. Addressing health issues and balancing hormones helps to promote a healthy body and supports your weight goals.
Here are the five hormonal body types.
Thyroid body type
Thyroid body types experience unexplained weight gain all over the body. Imbalanced thyroid levels can result from estrogen imbalance or impaired liver function and cause persistent body weight.
Adrenal body type
The adrenal body type tends to develop fat around the lower abdomen caused by elevated cortisol, an adrenal hormone released in response to stress. Relaxation techniques, good sleep hygiene, and the right diet benefit this hormonal body type.
Pancreas body type
The pancreas body type has a similar body shape to the adrenal body type and is the most common hormonal body type. Pancreas body types develop in response to metabolic imbalances triggered by high-carb diets and blood sugar imbalances.
Liver body type
The liver body type typically has a protruding and solid belly. Impaired liver function can imbalance essential hormones, leading to fat storage deposition around the abdomen.
Ovary body type
Ovary body types experience weight gain around the arms, thighs, and hips. Elevated levels of estrogen cause increased fat storage and lowered basal metabolic rate in women, making weight loss a challenge.

Key takeaways
Endomorphs have a slow metabolism and often develop excess body fat resulting in a large, round body frame. They can find it hard to gain muscle mass and to lose weight.
This body type is prone to metabolic imbalance and at higher risk of developing a hormonal body type. A low-carb diet and tailored exercise regimen help endomorphs to balance hormone levels, build muscle and lose weight.
FAQ
1. What are the three metabolic body types?
According to research, the three metabolic body types are endomorph, mesomorph, and ectomorph.
2. How do I know if I’m the endomorph body type?
If you have a large, round skeletal frame, find it hard to lose weight, and have larger bones than most people, you are most likely an endomorph body type.
3. What’s the difference between metabolic and hormonal body types?
Hormonal body types are characterized by imbalanced hormone levels due to factors including impaired liver function, diet, and exposure to environmental pollutants or stress. Your hormones determine body fat deposition, and imbalance can lead to persistent weight gain and inability to lose weight.
In contrast, metabolic body types are determined by your genetic predisposition, your metabolism, and your body’s overall energy needs.
Balancing hormones and addressing underlying health is the first step for hormonal body types to achieve their weight and fitness goals.
Take this body type quiz to figure out your body type.
4. What is the ectomorph body type?
Ectomorph body types have a small body shape and lean body composition. They often have narrow shoulders, flat chests, and less muscle mass than mesomorphs.
This body type indicates a fast metabolism. Ectomorphs burn calories quickly and can find gaining weight difficult. Ectomorphic types have lean muscles and low body fat.
5. What is the mesomorph body type?
Mesomorphs are generally of a medium-sized stature and have broad shoulders and a more rectangular bone structure than other types. Mesomorphic body types have moderate body fat and build muscle easily.
The mesomorph body type has a well-functioning metabolism and can lose weight quickly. This body type can achieve strong muscle growth by combining a low-carb diet with compound exercises and strength training.
6. What is the endomorph body type?
Endomorphs have a large, round body frame. They are more prone to a slower metabolism and excess fat than other metabolic body types. Endomorphic bodies can find it challenging to lose weight and build muscle.
This body type thrives on a nutritious low-carb diet like Healthy Keto. Avoiding processed foods, cakes, soft drinks, white bread, energy drinks, sports drinks, refined cereals, baked goods, and other sweets helps endomorphs to lose weight and support balanced hormone levels.
7. Are metabolic body types the same as hormonal body types?
No, metabolic and hormonal body types aren’t the same. Metabolic body types are determined by your genetics, energy needs, and autonomic nervous system.
Hormonal body types are a symptom of an underlying hormone imbalance resulting in excessive fat storage and altered body composition.
Previous blog
Ectomorph Body Type ExplainedNext blog
Mesomorph Body Type ExplainedTags

Popular
08/21/2024
47K views
05/22/2024
41.2K views
11/18/2024
244.1K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




