Eight Reasons You’re Gaining Weight on Keto

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How to Read Your Body
Learn to recognize common symptoms and uncover their underlying health issues
Understand the signs of nutrient deficiencies to manage your health
Explore the four metabolic body types and the core factors that influence them
Interpret your body's signals from head to toe to identify potential health concerns

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine

How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Understand the science behind intermittent fasting and its health benefits
Learn how fasting impacts metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance
Discover the four stages of intermittent fasting
Get practical tips for integrating fasting into your daily routine
Weight loss isn’t as simple as just increasing your fat intake and limiting carbs. There are many hormonal and metabolic factors that may be causing weight gain despite limiting your carbohydrate intake.
Let's look at eight reasons you’re gaining weight on keto and how to tweak your keto lifestyle for long-term weight loss success.
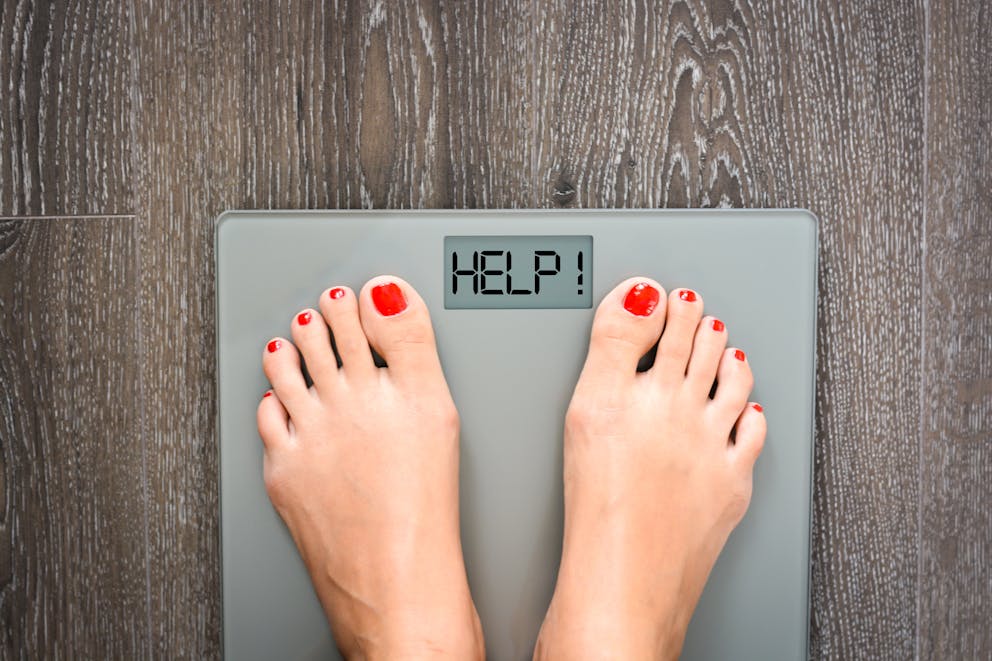

Eight reasons you’re gaining weight on keto
While many people have lost a considerable amount of weight on keto, some have difficulty losing weight or experience unexpected weight gain.
Your metabolic rate, hormone balance, and health status are unique to you and can significantly impact your weight status. The good news is that gaining weight on keto doesn’t mean a high-fat, low-carb diet isn’t right for you.
“What’s important to remember is that weight loss isn’t an indicator of health,” explains Dr. Berg. “You have to get healthy to lose weight, not lose weight to get healthy.”
Here are eight causes of weight gain on keto and the solutions to achieve a healthy weight.
1. Not staying in ketosis
One of the most common reasons for weight gain on keto is an inconsistent carb intake that causes your metabolism to flip-flop between fat-burning and using sugars as the primary energy source.
Keto success depends on limiting carb intake to keep insulin low, which triggers ketosis and primes your metabolism to break down fats.
Cheat days on keto aren’t a great idea and can quickly derail your weight loss efforts. Whenever you consume too many carbs, your insulin levels will spike, which inhibits fat burning and stimulates fat storage.
And, what’s more, it typically takes your body a few days to restart ketosis after consuming too many carbohydrates, which slows down keto-adaptation and can lead to weight gain.
To achieve consistent weight loss, it’s crucial to limit your net carb count to no more than 20 to 50 grams per day and consume plenty of healthy fats and moderate amounts of protein.
2. Stress
Stress is an often overlooked factor when it comes to weight gain.
When you experience stress, your adrenal glands release cortisol, a hormone that regulates metabolic processes to support the body's energy needs to sustain stressful periods.
While cortisol plays a vital role in your body’s stress response, prolonged stress can lead to chronically elevated cortisol, which has been found to contribute to weight gain.
Evidence published in Current Obesity Reports suggests that cortisol stimulates fat storage, especially around the abdomen. This explains why prolonged stress can cause an adrenal body type characterized by unexplained weight gain and belly fat.
A healthy lifestyle, adequate sleep, regular exercise, and relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and long walks can calm the nervous system and may help counteract cortisol’s weight-gain effects.

3. Slow metabolism
Individuals with a slow metabolism burn fewer calories than those with a higher metabolic rate.
There are many reasons for a slow metabolism, including menopause, hypothyroidism, genetic predisposition, hormone imbalances, and frequent dieting.
If you suspect you have a slow metabolism, monitoring your fat intake on keto is essential. Fat contains almost twice as many calories as carbs, and it’s easy to consume excessive amounts of fats on a high-fat diet, which can quickly lead to weight gain.
Boosting your metabolism doesn’t really work, but you can improve your metabolic flexibility, a measure of how quickly your body adapts to using fat instead of sugars as a primary fuel source.
Combining keto with intermittent fasting, a meal schedule that cycles between fasting periods and periods of eating, forces your metabolism to burn stored body fat for energy. This stimulates increased production of fat-oxidizing enzymes in the liver, enhancing your metabolism's ability to utilize body fat as a primary fuel source.
4. Not consuming enough nutrients
Achieving healthy and long-lasting weight loss with keto requires more than limiting carbs and increasing fats.
There are many fast foods, junk food, and processed foods that are low in carbs and high in fat, but these foods won’t help you lose weight and may, in fact, cause weight gain.
Research published in Clinical Nutrition confirms that a diet high in processed foods is linked to overeating, nutritional deficiencies, and metabolic imbalances, which can significantly increase the risk of obesity.
To promote healthy weight loss, it’s vital to follow a nutrient-dense Healthy Keto® diet that focuses on minimally processed keto-approved whole foods, including grass-fed beef, wild-caught fish and game meats, seafood, high-fat dairy, and organic vegetables.
5. Alcohol
Although pure alcohol has zero carbs, drinking alcoholic beverages can quickly lead to weight gain.
Because alcohol is a toxic compound, the liver prioritizes alcohol detoxification over other metabolic processes, including fat burning.
In addition, most alcoholic beverages are high in carbs and often mixed with sugary soft drinks or fruit juices. Even small amounts of alcohol can stop weight loss and ketosis, and it can take 48 to 72 hours to restart fat-burning after drinking.
Alcohol is a common reason for weight gain on keto, and it’s best to minimize or avoid alcohol as much as possible to maintain ketosis and promote metabolic health.
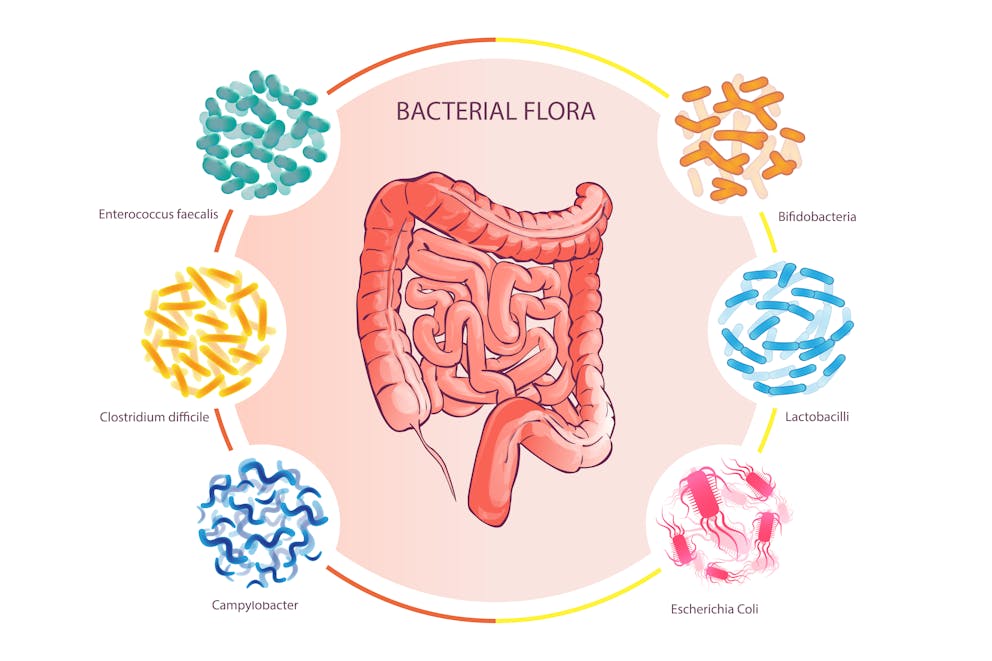
6. Imbalanced intestinal microflora
Although it may not seem obvious, your intestinal microflora can significantly impact your weight status.
An imbalance or disruption in the composition of the gut microflora, also known as dysbiosis, has been found to disrupt fat metabolism, increases the risk of insulin resistance, and may cause low-grade inflammation, all of which has been linked to weight gain.
According to a study published in Microorganisms, “A shift from the healthy symbiosis between the microbiota and the host to persistent dysbiosis may contribute to excess fat deposition. Obese patients are associated with a low bacterial gene count, meaning a relatively poor gut microbiota.”
Dysbiosis can develop as a result of several factors, including:
A diet high in refined carbs, sugars, and processed foods
Lack of dietary fiber and prebiotic foods
Alcohol
Stress
Gastrointestinal infections
You can promote a diverse intestinal microflora by consuming pre- and probiotic-rich foods such as garlic, onions, asparagus, artichokes, kefir, and kimchi.
In addition, it’s crucial to restore your intestinal microflora with a high-quality probiotic supplement if you have recently been prescribed antibiotics.
7. Lack of exercise
Regular exercise is important for metabolic health, especially if you are gaining weight despite following a healthy diet low in carbs.
Muscles are more metabolically active and burn more calories than most other tissues, even at rest. Building muscle mass can counteract a slow metabolism and may prevent weight gain.
Regularly including high-intensity interval training in your keto lifestyle can help you lose fat and gain muscle simultaneously.
8. Underlying health issues
Underlying health issues can significantly impact weight, fat distribution, and body composition.
“Categorizing different body types based on potential underlying health problems is very helpful in finding effective solutions that improve well-being and support healthy weight loss,” says Dr. Berg.
Individuals with thyroid gland issues often experience unexplained weight gain all over the body, a hallmark of the thyroid body type.
In contrast, people with protruding bellies are more likely to fit the liver body type, typically associated with poor liver function, excessive alcohol consumption, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease.
While Healthy Keto is an excellent diet to support liver and thyroid health, it’s essential to address and manage any underlying health conditions to promote overall health and achieve weight loss goals.
Watch the video below to learn what can cause rapid weight gain on keto and how to prevent it.
What is ketosis?
Ketosis is a metabolic state during which your body relies on ketones as a primary energy source.
When the liver burns fat instead of sugars for energy, it generates large amounts of ketones, a group of organic compounds that can be utilized as a fuel source by the brain, heart, muscles, and other tissues.
Ketosis can be achieved by restricting carbohydrate intake to no more than 20 to 50 grams of net carbs per day and obtaining the majority of calories from healthy fats and moderate amounts of protein.
Insulin regulates blood sugar control and is a key metabolic hormone that stimulates fat storage and inhibits fat burning. Restricting carbs keeps insulin low, which liberates stored body fat and shifts your metabolism into fat-burning mode.
A low-carb, high-fat diet, also known as the ketogenic diet, doesn't just support weight loss but has been linked to several profound health benefits.
A recent study published in Nutrients surmises, “The ketogenic diet shows promise in helping patients lose weight, reverse the signs of metabolic syndrome, reduce inflammation, improve lipid profiles, and potentially increase longevity and brain function.”

Is it possible to gain weight on keto?
Yes, it’s possible to gain weight on keto.
How easily you lose or gain weight depends on your diet, genetics, stress, activity levels, sleep habits, and hormone balance.
Because of this complexity, there is no one-fits-all keto diet approach, and you may have to adjust your keto lifestyle based on your individual needs to prevent weight gain.
Keto is a high-fat diet, and it’s possible to consume too many calories, exceeding your daily caloric energy needs, which can lead to weight gain even if your metabolism is in ketosis.
It’s important to remember that the liver will always burn dietary fats before utilizing stored body fat and consuming too many high-fat foods can stop weight loss and cause weight gain.
While counting calories isn’t really necessary on keto, tracking your fat and calorie intake for a few days may be beneficial to check if you are eating excessive amounts of fat, which may provide you with more calories than your body needs.
Watch the video below to learn why you aren’t losing weight on keto.
How long does it take to start losing weight on keto?
How long it takes to start losing weight on keto depends on how quickly your body adapts to the ketogenic diet, your health status, activity levels, metabolic rate, and previous dietary habits.
Most people experience rapid weight loss during the early phases of keto. This typically results from fluid loss, a side effect of keto-adaptation.
Glycogen, a form of glucose bound to water that’s stored in muscles and the liver, is depleted within the first week of ketosis, which eliminates large amounts of fluids and explains why keto can cause significant weight reduction straightaway.
However, once glycogen stores are exhausted and your body relies on ketones as an energy source, weight loss often slows down.
While some individuals can lose as much as two to three pounds per week on keto, a slower weight-loss rate of around one pound per week is more common.
Weight loss can be concealed. Muscle mass is heavier than fat mass, and you may not see a weight reduction on keto if you exercise regularly.
Losing inches but not losing weight is an excellent indicator that your keto diet plan and exercise routine are working for you.

Key takeaways
The most common reasons you’re gaining weight on keto are overeating fat, an inconsistent carb intake, lack of exercise, and stress.
In some cases, underlying health issues such as low thyroid function, liver problems, or an imbalanced composition of the intestinal microflora can disrupt metabolic pathways and prevent weight loss.
Combining keto with intermittent fasting and addressing any potential underlying health issues are crucial steps to promote effective fat burning and achieving your weight loss goals.
FAQ
1. Why am I gaining weight on a keto diet?
Weight gain on keto can have several reasons, including consuming too much fat and calories, stress, alcohol, lack of exercise, a slow metabolism, and underlying health issues such as low thyroid function or liver damage.
2. How long does it take to lose weight on keto?
It’s common to experience rapid weight loss during the first two weeks of keto due to glycogen shedding and fluid loss. Once glycogen stores are depleted, your metabolism switches to using fat as a primary fuel source, and most people report a weight loss rate of one to two pounds per week.
3. Is it normal to gain weight at first on keto?
While most people lose weight when starting keto, some are experiencing weight gain. This typically results from consuming too much fat and frequent snacking on high-fat foods.
Fat is high in calories, and excessive consumption can quickly exceed your daily energy requirements, leading to weight gain even if you are in ketosis.
4. Should I weigh myself every day on keto?
It’s not recommended to weigh yourself every day on keto. Weight can fluctuate due to fluid retention, which can be frustrating and demotivating.
It’s best to avoid weighing yourself frequently and instead pay attention to how you feel. Improved energy levels, better sleep, and mental clarity indicate that keto is working, which will promote a healthy weight in the long run.
5. Can you accidentally gain weight on keto?
You can accidentally gain weight on keto by consuming too much fat and frequent snacking. If you gain weight on keto, it’s important to monitor your fat intake to avoid overeating and limit snacks.
6. Why am I gaining weight on a low-carb diet?
There are many reasons why you may be gaining weight on a low-carb diet. Snacking, consuming too many calories, alcohol, and lack of muscle mass are the most common culprits of weight gain on keto.
7. Why am I hungry and gaining weight on keto?
Feeling hungry and gaining weight on keto can be a sign that you aren’t always in ketosis. It’s important to consistently limit your carb intake to avoid flip-flopping between burning fat and using sugars as a primary fuel source which triggers cravings and causes weight gain.
8. Why did I gain 3 pounds on keto?
If you gain weight on keto, you may consume too many carbs, which triggers the deposition of glycogen, a storage form of glucose.
In order to store glycogen in muscles and the liver, the body retains significant amounts of water, a common reason for rapid weight gain on keto.
9. Why am I gaining weight when I barely eat?
Unexplained weight gain can indicate underlying health issues or hormonal imbalances.
Stress, low thyroid function, and liver damage can disrupt metabolic processes and influence body composition. It’s essential to address and manage any potential health problem to promote your metabolic health and achieve weight loss goals.
10. Why am I bloated on keto?
Bloating on keto can indicate sluggish gallbladder function, which can cause poor fat absorption and gastrointestinal issues.
In some cases, bloating can also be a side effect of consuming keto sweeteners, including sugar alcohols, or may be linked to electrolyte imbalance which can trigger water retention and cause abdominal distention.
11. Can too much protein on keto cause weight gain?
Excess protein can be converted into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, which can raise blood sugar, inhibit fat-burning, and lead to weight gain.
12. Can too much fat on keto cause weight gain?
Yes, consuming too much fat on keto can quickly lead to weight gain. Fat contains almost twice as many calories as carbs, and consuming excessive amounts can exceed your daily energy needs, which leads to weight gain even if you are in ketosis.
13. Can I have a cheat day on keto?
Cheat days on keto will likely disrupt fat-burning and contribute to weight gain. And, what’s more, it can take several days to restart ketosis after a carb-rich cheat meal, which explains why one cheat day can quickly undo the metabolic benefits of keto.
Previous blog
Is Oat Milk Keto-Friendly? Dairy-Free Milk Alternatives
Popular
08/21/2024
46.9K views
05/22/2024
41.2K views
11/18/2024
244.1K views
03/18/2024
11/21/2022




